Utah Passes Blockchain Law, Removes Bitcoin Reserve Clause

Utah lawmakers have passed H.B. 230, the “Blockchain and Digital Innovation Amendments” bill, designed to regulate digital assets, but they excluded a clause that would have enabled the state to invest in Bitcoin.
The original version of the bill included a Bitcoin reserve clause, but this provision was removed before the final vote.
The Utah Senate passed the bill with a 19–7 vote, after which the House of Representatives approved the Senate’s amendments and officially enacted the legislation with a 52–19 vote, while four members abstained. The bill was introduced by Republican lawmakers Jordan Teuscher (House of Representatives) and Senator Kirk Cullimore.

Related: Utah Legislature Advances Bill to Invest Public Funds in Crypto
Despite the removal of the Bitcoin reserve clause, the bill introduces several key protections for the blockchain industry. It prohibits state and local authorities from restricting the acceptance of digital assets and safeguards citizens' rights to run a node and participate in staking without requiring a money transmitter license.
Additionally, the bill limits local governments from imposing unjustified zoning restrictions or noise regulations aimed at mining companies operating in industrial areas.
The passage of this law aligns with the U.S. administration’s March 6 decision to establish a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve and a Digital Asset Stockpile, highlighting the government’s growing interest in cryptocurrencies.
However, Utah Governor Spencer Cox has not yet stated whether he will sign the bill. If approved, it will take effect on May 7, 2025.
Other States Are Moving Toward Bitcoin
While Utah rejected the idea of a Bitcoin reserve, several other states are actively integrating cryptocurrency into public finance.
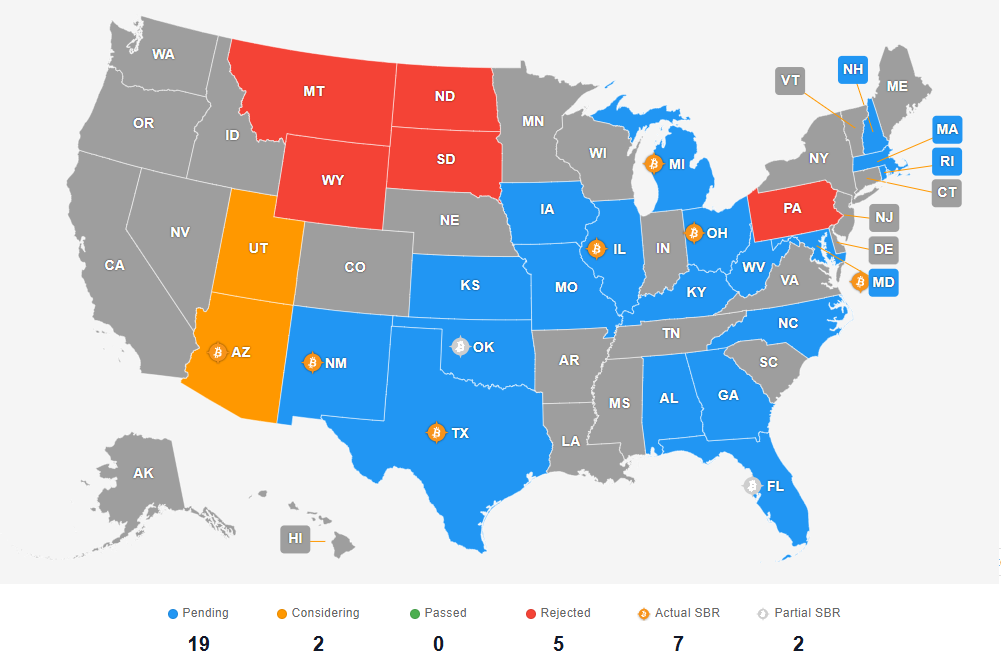
Texas and Arizona are at the forefront. Notably, the Texas Senate recently approved a Bitcoin reserve bill (25–5). Senator Charles Schwertner, who introduced the bill, emphasized that Bitcoin’s fixed supply and inflation-resistant properties make it a valuable asset for the state's financial future.
Related: 5 U.S. States Considering BTC Reserves
In Arizona, lawmakers are reviewing SB 1025, which has already passed its 3rd reading in the Senate. The proposal seeks to allocate up to 10% of state funds into Bitcoin and other digital assets.
Oklahoma is also taking steps toward crypto adoption. The Government Oversight Committee has approved HB 1203, which would establish a strategic Bitcoin reserve.
However, not all states are on board with cryptocurrency investments. Montana, South Dakota, Pennsylvania, North Dakota, and Wyoming have rejected similar proposals, citing Bitcoin’s high volatility as a key concern.
As of now, Bitcoin reserve initiatives remain under review in 18 states, including Kansas, Iowa, Missouri, Illinois, Florida, Massachusetts, and Michigan.
What Does This Mean for the Crypto Community?
Utah’s decision to exclude a Bitcoin reserve reflects a cautious approach to integrating cryptocurrency into state finances. While H.B. 230 implements key measures supporting the blockchain industry, the absence of a Bitcoin reserve clause signals ongoing concerns and regulatory hesitation among lawmakers.
This situation highlights that the U.S. is still refining its crypto regulatory strategy. Over the next few years, lawmakers will likely engage in further debates and introduce potential legislative adjustments, particularly as the federal government’s interest in digital assets continues to grow.
Ultimately, the future of Bitcoin policy will likely depend on economic conditions and market developments throughout the year.
The content on The Coinomist is for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as financial advice. While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of any content. Neither we accept liability for any errors or omissions in the information provided or for any financial losses incurred as a result of relying on this information. Actions based on this content are at your own risk. Always do your own research and consult a professional. See our Terms, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers for more details.