What Is Babylon and How It Plans to Put Idle Bitcoin to Work?

Integrating Bitcoin into DeFi and increasing its use cases is a major focus in crypto. Babylon is a leading project in this niche, aiming to allow Bitcoin holders to put their assets to work by staking.
On this page
How does this work exactly, and what’s the point of using Bitcoin on other chains? In this article, we’ll review Babylon, its current status, and the solutions it provides.
Why Can’t You Earn from Bitcoin Like You Can from Proof of Stake Coins like Ether?
To understand what Babylon is about, you need to know a little about the use cases of coins operating on different types of blockchains. The Bitcoin Network uses the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism while blockchains like Ethereum and Solana use the Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
These PoW and PoS systems are needed to incentivize people to join the network and provide resources to check and verify transactions. In return, participants receive rewards, usually in the network’s native coin.
Bitcoin’s way to ensure network security is to drive competition where miners solve tough math puzzles to verify transactions and add them to the blockchain.
The process is energy-heavy. Since so much electricity and resources are spent to solve these puzzles, it would be incredibly hard for someone to take over the network and change any transaction history.
PoS works differently: it relies on staking and validators instead of miners. They “stake” or lock up some of their crypto as collateral to verify transactions. When they stake their crypto, they essentially put it on the line. If they try to validate a false transaction or act dishonestly, the system will “slash” or take away staked crypto as punishment.
It’s like a security deposit in case they misbehave.
By design, Bitcoin has limited use cases. It can’t be used in decentralized finance (DeFi) the same way as Proof-of-Stake tokens can.
Here’s what we mean.
Holders of Proof-of-Stake coins can lock their assets on the network directly and earn yield for securing the system. Bitcoin itself is not used to secure the Bitcoin chain.
What Is Babylon: Self-Custodial Bitcoin Staking Protocol?
Babylon Labs’ mission is to unlock idle Bitcoins and allow their use in Proof of Stake blockchains. In its litepaper, Babylon mentions that most of yield-generating activities, including DeFi lending and security staking happen on PoS blockchains.
Over time, solutions have been developed to bring Bitcoin to PoS. Since the Bitcoin Network doesn’t directly communicate with networks like Ethereum, Bitcoin can be moved to other blockchains through bridges and/or by sending it to a centralized custodian.
The custodian manages the Bitcoin and may issue wrapped tokens (like WBTC) on another blockchain.
WBTCs represent Bitcoins on other chains and are backed 1:1 by Bitcoin. They basically allow Bitcoins' use in decentralized applications or for other purposes outside the Bitcoin network.
But WBTC is not a perfect way to move Bitcoin to other chains because of the custodial or smart contract vulnerability risks.
And there Babylon comes into the picture.
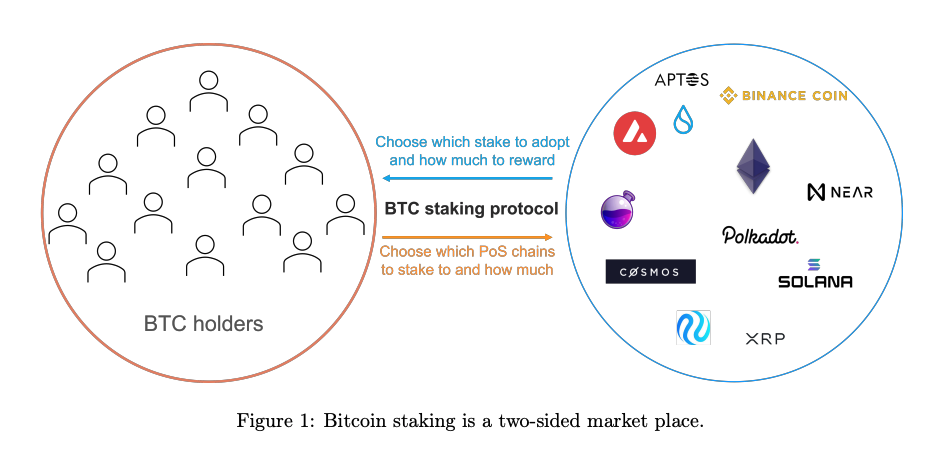
How Does Babylon Work?
Babylon’s Bitcoin staking protocol allows Bitcoin holders to stake their Bitcoin for Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains without the need for third-party bridges or custodians. The staked Bitcoins help secure PoS chains, while Bitcoin holders can earn yield on their capital.
To make this possible, Babylon uses two key protocols: the Bitcoin Timestramping Protocol and the Bitcoin Staking Protocol.
Timestramping is essentially marking the exact time when a Bitcoin transaction occurs. Each transaction is added to a “block,” and each block has a timestamp. These blocks are then linked together in a chain, which is why it's called a blockchain.
Babylon’s Timestramping Protocol ensures synchronization between PoS blockchains and Bitcoin, acting as a foundational element for the Staking Protocol.
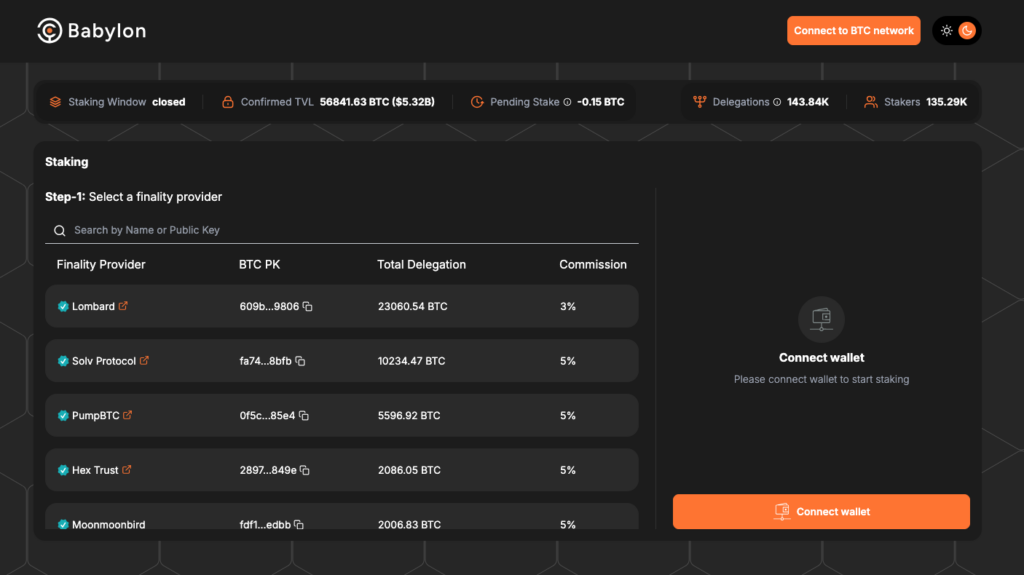
The Staking Protocol is where Bitcoin holders interact with the system and stake their tokens. First, they send a staking transaction to the Bitcoin chain, locking their coins in a self-custodian vault.
Only the user can unlock their coins using their private keys. The unbonding* of coins (*the process where the user's coins are “uncoupled” from the validator coins) is available at any time, allowing users to access their funds whenever they choose.
Once the transaction is completed, the user can begin validating transactions on the PoS blockchain and earn staking rewards in return.
Where Does Babylon's Development Stand?
Babylon was co-founded in January 2022 in January 2022 by Stanford Professor David Tse and Dr. Fisher Yu. In July 2023, the project launched Version 1.0 of its litepaper, outlining its mission and solutions.
To date, Babylon has raised $96 million from investors such as Polychain Capital, Hack VC, Polygon Ventures, Binance Labs, Bullish Capital, Paradigm, and others.
The protocol was developed using the Cosmos SDK toolkit and launched on the testnet in February 2024. Within 48 hours of launch, the testnet saw over 100,000 stakers, signaling high demand for custodial Bitcoin staking.
Babylon adopted a phased approach to the mainnet launch in order to implement Bitcoin staking gradually and carefully. Phase-1 of the mainnet went live on August 22, 2024, with an initial cap of 1,000 bitcoins.
In phase one, Bitcoin holders began locking their Bitcoin to convert it into staсkable assets. Phase two focused on the demand side by introducing the Babylon PoS chain as the first recipient of Bitcoin's security. In phase three, Bitcoin multi-staking will be enabled, allowing holders to secure multiple PoS systems simultaneously.
As of January 2025, the project has achieved phase 2.
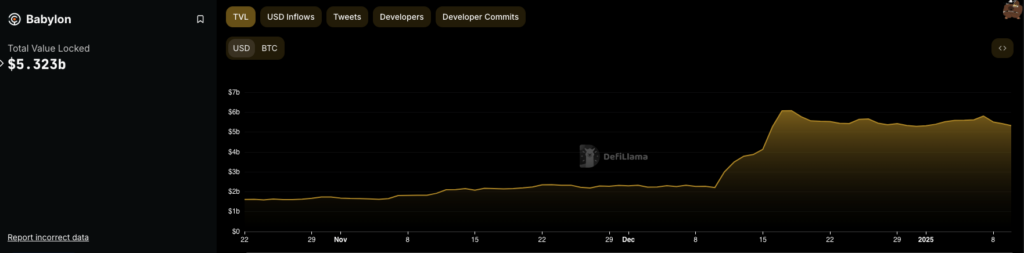
Babylon launched its Phase-2 testnet with an upgraded staking app on January 8, 2025. The protocol has seen rising demand.
According to DeFiLlama, Babylon is currently the largest project in the Bitcoin ecosystem, with over $5.3 billion in total value locked (TVL).
Babylon Project’s Future and Potential Airdrop
Babylon is steadily advancing with its phased mainnet launch, though there’s no official word yet on whether users can expect a native token release. Despite this uncertainty, Babylon has positioned itself as one of the most promising projects in the Bitcoin staking ecosystem.
By focusing on integrating Bitcoin into Proof-of-Stake (PoS) systems, Babylon aims to unlock new use cases for Bitcoin holders, enabling them to earn rewards while maintaining security.
That said, Bitcoin staking is a relatively new sector within the crypto space, and it’s evolving rapidly. Babylon is not alone in this effort — other emerging protocols like Lombard and Lorenzo are also gaining traction, offering alternative approaches to leveraging Bitcoin for staking.
FAQ
- What Is Babylon?
Babylon is a self-custodial Bitcoin staking protocol that allows Bitcoin holders to stake their Bitcoin on Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains. This enables Bitcoin to secure PoS systems while holders earn rewards for their contributions. It operates as a security marketplace, connecting BTC holders with PoS chains.
- When was Babylon launched?
Babylon was founded in January 2022. Its testnet launched in February 2024, and the phased mainnet rollout began on August 22, 2024. The project is currently in phase two as of January 2025.
- Is there a Babylon token?
There is no official information yet about a native token launch. The team has not confirmed whether such an offering is planned.
- What are the advantages of Babylon?
Unlike staking solutions that rely on centralized custodians or smart contracts to manage Bitcoin, Babylon operates without intermediaries. Bitcoin remains under the self-custody of users, reducing custodial and smart contract risks.
The content on The Coinomist is for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as financial advice. While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of any content. Neither we accept liability for any errors or omissions in the information provided or for any financial losses incurred as a result of relying on this information. Actions based on this content are at your own risk. Always do your own research and consult a professional. See our Terms, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers for more details.

























